GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
• Dim. mm approx (HxLxW) : 700x1000x150 – (470 with the base)
• Weight approx. kg 25
• Input power supply: AC 220V±10% 50 Hz
• Working temperature: -40℃ ~ +50℃.
MAIN CHARACTERISTICS
The simulator analyses all the phases of the refrigeration cycle. In particular:
– Relations between temperature and pressure in the refrigerant
– Operation of the compressor
– Operation of the condenser
– Pressure switches
– Temperature regulation
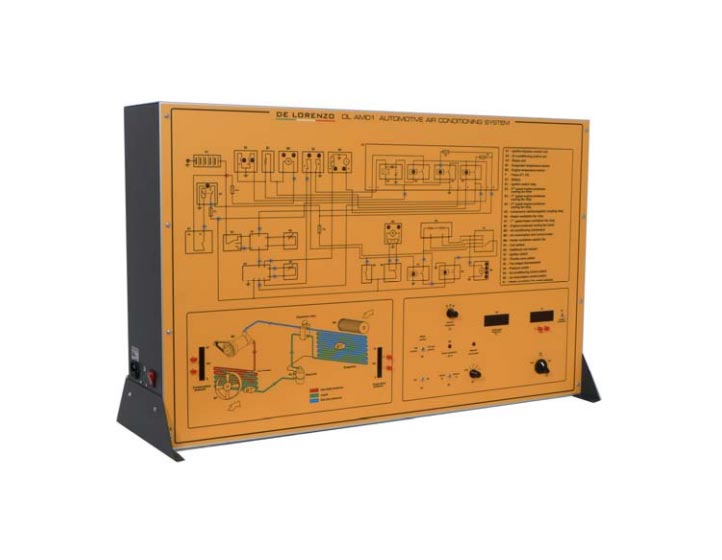
This vertical frame bench-top trainer is specially designed to show to students how automotive systems work.
The simulator consists of a panel operated by the support of a computer with a coloured silk-screen diagram that clearly shows the structure of the system and allows the location of the components on it.
The display of the information available on the computer screen allows the continuous control of the educational system.
The operational conditions can be entered by the students and the insertion of faults can be carried out through the computer by the teacher.
The trainer is supplied with a CAI Software and the supported documentation guides the students to the study and the performance of the simulation exercises.
All components installed and given leads are made to protect the safety of the students.
AIR CONDITIONING FOR AUTOMOBILES
This simulation panel is properly designed and realized to allow an easy and complete learning of the techniques and of the electro-mechanical, and electronic devices that are used for the regulation and control of automotive air conditioning.
To cool the external air, refrigerating compressor based systems are exclusively used.
The compressor activated by the engine compresses the refrigerant, which consequently warms up; in the condenser the working fluid is cooled until it reaches the liquid phase.
The cooling is obtained by giving heat to the exterior in the zone around the compressor.
The cooled fluid expands in the expansion valve and in the evaporator and is transformed in gas.
The heat necessary for such transformation is subtracted from the entering cool air.