Theoretical topics:
• The bio-potentials and their measurement
• The heart and the measurement of its electrical activity
• The muscles and the measurement of their electrical activity
• The brain and the measurement of its electrical activity
Circuit blocks:
• Electrocardiograph: to record the potentials that are generated on the surface of the body during the process of stimulating the cardiac musculature
• Electroencephalograph: to record the cerebral electrical activity
• Electromiograph: to record the electrical activity of the muscles and of the relevant nervous fibres
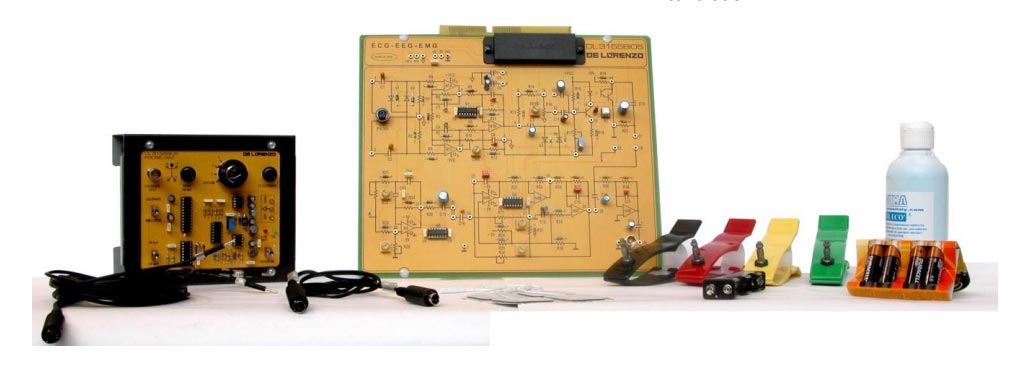
ECG SIMULATOR
This is an external block which is provided together with DL 3155BIO5.
ECG-SIMULATOR provides the power supply to the ECG-EEG-EMG panel in order to meet the requirements for patient safety. Moreover a simulated ECG signal is generated with amplitude of 4 mV pp. ECG signals are available with two frequency rates, such as 60 or 120 bpm (beats per minute).
ECGSIMULATOR is mandatory when an actual ECG measurement is performed on a patient. In fact the external block provides a multiple switching which permits to select the correct LEAD when electrodes are placed on the patient. A calibration fixed level of 1 mV can be selected to perform ECG calibration.
This board does not substitute the medical device under study. The results of the experiments have no medical value. They are just for demonstration purposes.
ECG – EEG – EMG
The bio-electrical potentials are currently recorded as a routine in several specialities of the modern clinical practice.
Such potentials are the result of an electrochemical activity of a class of cells, named excitable cells, that form the nervous, muscular and glandular tissues.
The measurement of the bioelectrical phenomena is, therefore, used to learn the electrochemical activity of such tissues.
The most widely used bioelectrical signals, such as the electrocardiogram, the electroencephalogram and the electromiogram, have a very low amplitude and are generated by sources that have a high internal impedance.
In this course we will study first of all the general specifications of the systems for the measurement of bioelectrical signals and subsequently the characteristics of some special systems.
This course comprises a further instrument, the ECG SIMULATOR, which is mandatory to provide power supply to the circuit and provides a simulated ECG signal for performing experimental activity.