TRAINING OBJECTIVES
It is possible to simulate the behaviour of components and systems, on the basis of the operating conditions which can be monitored directly on the panel or through Personal Computer by teacher and students.
The Personal Computer constantly keeps under control the simulation in progress and displays its behaviour through analog and digital signals and meters; in this way the student, through measurements and tests, can go on with the troubleshooting.
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
The experimentation on the photovoltaic systems (described here under) is organized as follows:
• Possibility to simulate several values of the solar radiation intensity (W/m2)
• Possibility to simulate several values of the photovoltaic cells temperature
• Possibility to change the electrical load of the above‐ mentioned photovoltaic systems
• Detection of the characteristic voltage‐current (V‐I), supplied by the photovoltaic systems, as a function of solar radiation intensity and cells temperature
• Detection of the characteristic voltage‐power (V‐P), sup‐ plied by the photovoltaic systems, as a function of solar radiation intensity and cells temperature
• Evaluation of the conversion efficiency (radiating energy‐electric power) of the photovoltaic systems
The experimentation on the thermal panel with liquid circulation is organized as follows:
• Possibility to simulate several values of the solar radiation intensity (W/m2)
• Possibility to simulate several values of the temperature of the thermal‐carrier liquid at the panel’s entrance
• Possibility to change the thermal‐carrier liquid capacity through the thermal panel
• Evaluation of the thermal‐carrier liquid temperature at the panel’s exit, as a function of the solar radiation intensity and of the entrance temperature
• Evaluation of the conversion efficiency (radiating energy‐ electric power) of the thermal panel
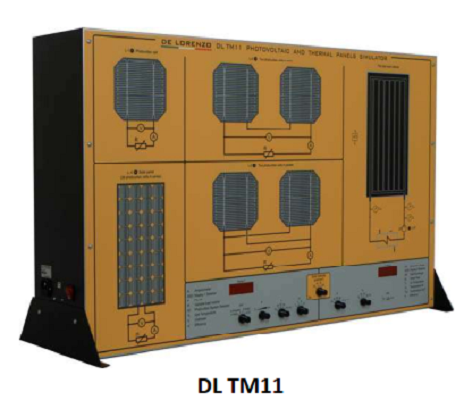
PHOTOVOLTAIC AND THERMAL PANELS
The simulator allows the study, the performing of experiments and the troubleshooting for the following systems:
• Photovoltaic silicon single crystal cell, squared, side 135 mm
• Two photovoltaic cells with series connection
• Two photovoltaic cells with parallel connection
• Panel composed of 36 photovoltaic cells with series connection
• Thermal panel with liquid circulation
These systems are reproduced on the panel, through a colour representation which allows a complete analysis of the fluid circuit, of its components and of the electrical/electronic circuit for control and regulation.